Blockchain is one of those buzzwords that everyone talks about, but few really understand. If you’ve ever wondered what it actually is — beyond the hype — this blog post is for you.
🧱 What Is a Blockchain?
A blockchain is like a digital ledger — a record of transactions that is:
- Public: Everyone can see the data (on public blockchains)
- Decentralized: No single person or company controls it
- Immutable: Once something is written, it can’t be changed
Imagine a notebook shared among thousands of people. Everyone writes in it at the same time, and everyone has a copy. That’s the basic idea.
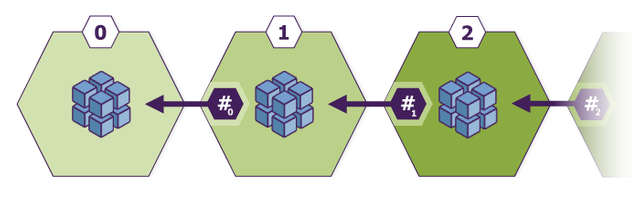
🔁 How It Works: Block by Block
Here’s a super simplified breakdown:
- Someone makes a transaction (e.g., sending Bitcoin)
- The transaction is broadcast to a network of computers (called nodes)
- The nodes verify the transaction using math and rules
- Once verified, the transaction is grouped into a "block" with others
- This block is added to the chain of previous blocks (the blockchain)
Each block is connected to the one before it, forming a secure chain — hence the name.
🔐 What Makes It Secure?
Two main things keep blockchain safe:
- Cryptography: Complex math equations protect the data
- Decentralization: There’s no single point of failure
To hack a blockchain, you’d need to control more than half of the network — almost impossible on big public chains like Bitcoin.
⚙️ What Is a Smart Contract?
Smart contracts are self-executing programs stored on the blockchain. They run automatically when certain conditions are met — no middleman needed.
Example: You rent a car with crypto → the smart contract unlocks the car once payment is received.
💡 Why It Matters
Blockchain isn’t just for crypto. It’s being used for:
- Finance (DeFi)
- Voting systems
- Supply chains
- Digital identity
- Ownership of art and media (NFTs)
❓ Common Misconceptions
- “It’s only for criminals” – Not true. Most use cases are legal and innovative.
- “It wastes too much energy” – Some blockchains do (like Bitcoin), but others use eco-friendly models (like Proof of Stake).
- “It’s completely anonymous” – It’s pseudonymous. Transactions are public but tied to wallet addresses, not names.
Thank you for sharing on steem! I'm witness fuli, and I've given you a free upvote. If you'd like to support me, please consider voting at https://steemitwallet.com/~witnesses 🌟
Downvoting a post can decrease pending rewards and make it less visible. Common reasons:
Submit